(click on the image for a larger version)
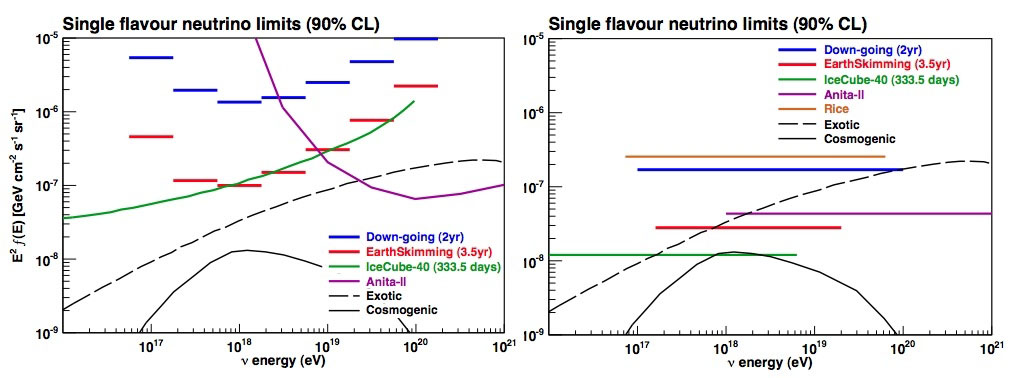
(The differential flux (left side) and the integrated flux (right side) limits set by Auger.)
The Pierre Auger Observatory located in Argentina is designed to observe high energy cosmic rays. Fortuitously, the Observatory is able to search for high energy neutrinos where its detection capabilities are comparable to that of neutrino-dedicated observatories. Due to the small cross section, neutrino-induced air showers are likely to occur deep in the atmosphere. Hence, deeply penetrating inclined air showers are the prime candidates. In addition, it is also possible to have tau-neutrinos to undergo charge current interactions inside the Earth’s crust, produce a tau lepton that emerges to the Earth’s surface and decay in the atmosphere, initiating an Earth-skimming air shower. With 2 to 3.5 years of data taking, no events have been discovered so far. However, the limits are approaching closer and closer to the nearly guaranteed Cosmogenic model range, which are predictions coming from the interaction of high energy cosmic rays with the photon background.
– Eun-Joo Ahn